Radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive element, poses significant health risks yet remains largely under-discussed. This colorless, odorless gas emerges from the decay of uranium in soil and rock, infiltrating homes and buildings. Understanding radon is crucial, not just for homeowners and builders, but for everyone concerned with public health and safety. This article offers an exhaustive insight into radon gas, covering its nature, sources, health risks, detection methods, and mitigation strategies. It aims to provide readers with essential knowledge, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding radon in their environments.
Contents
- 1 What is Radon Gas?
- 2 Sources of Radon Gas
- 3 Health Risks Associated with Radon Exposure
- 4 Detecting Radon Gas in Your Environment
- 5 Legal Standards and Safety Regulations
- 6 Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
- 7 Case Studies on Radon Gas Incidents
- 8 Future of Radon Gas Research and Technology
- 9 The Radon Gas Challenge
What is Radon Gas?
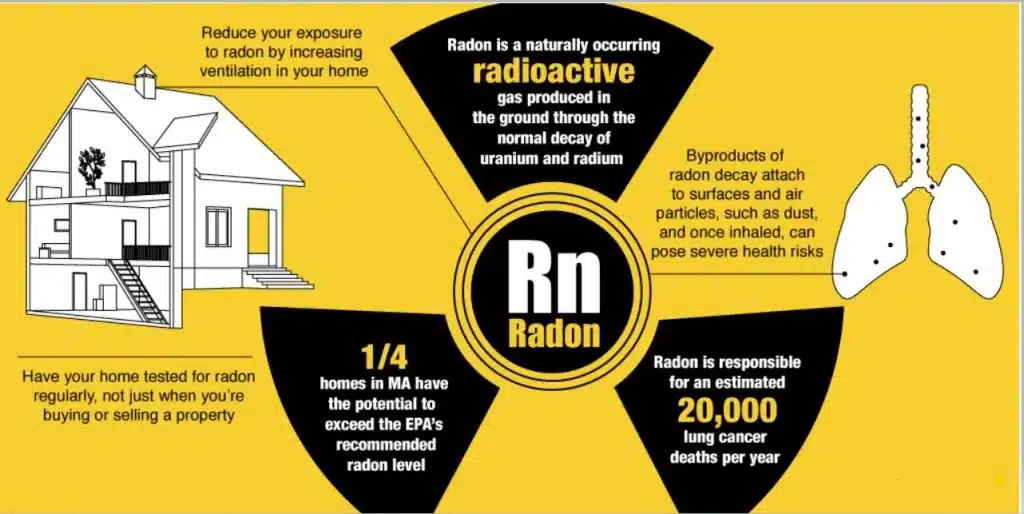
Radon is a chemically inert, radioactive gas that originates from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, water, and rocks. Invisible to the naked eye and undetectable by smell, radon gas can accumulate indoors, especially in lower areas like basements and ground floors. It’s part of the earth’s natural radioactive decay process, and its presence varies depending on the local geology.
Radon is omnipresent in the environment, but its concentration levels vary widely. Outdoor radon levels are generally low and pose little risk; however, when radon gas enters enclosed spaces like homes, it can accumulate to high concentrations, becoming a health hazard. Factors such as building materials and ventilation influence indoor radon levels.
Sources of Radon Gas
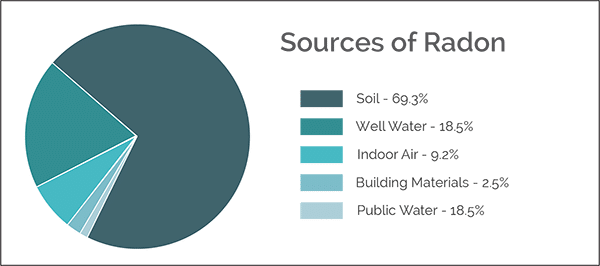
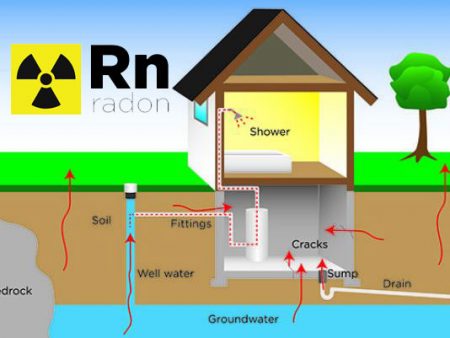
The primary source of radon is the decay of uranium in the earth’s crust. It naturally seeps through the ground into the air, where it usually disperses harmlessly. However, when it enters buildings through cracks in floors or walls, gaps in service pipes, or other openings, it can accumulate and reach harmful levels.
Apart from natural geological formations, human activities can also contribute to radon levels. Activities like mining and industrial processes that disturb the earth’s crust can release radon. Furthermore, building materials like granite or certain concrete, which contain trace amounts of uranium, can also emit radon, albeit to a lesser extent than geological sources.
Health Risks Associated with Radon Exposure

Short-term exposure to radon typically doesn’t lead to immediate health symptoms. However, the real danger lies in long-term exposure, which significantly increases the risk of lung cancer. Radon decay particles can become trapped in the lungs, where they continue to break down, releasing radiation that damages lung tissue.
The risk of lung cancer from radon exposure is dependent on several factors, including the level and duration of exposure, whether the individual smokes, and their overall health. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, and smokers exposed to high levels of radon have a much higher risk of developing lung cancer. It’s essential to understand these risks and take appropriate measures to reduce exposure, especially in areas known for high radon levels.
Detecting Radon Gas in Your Environment
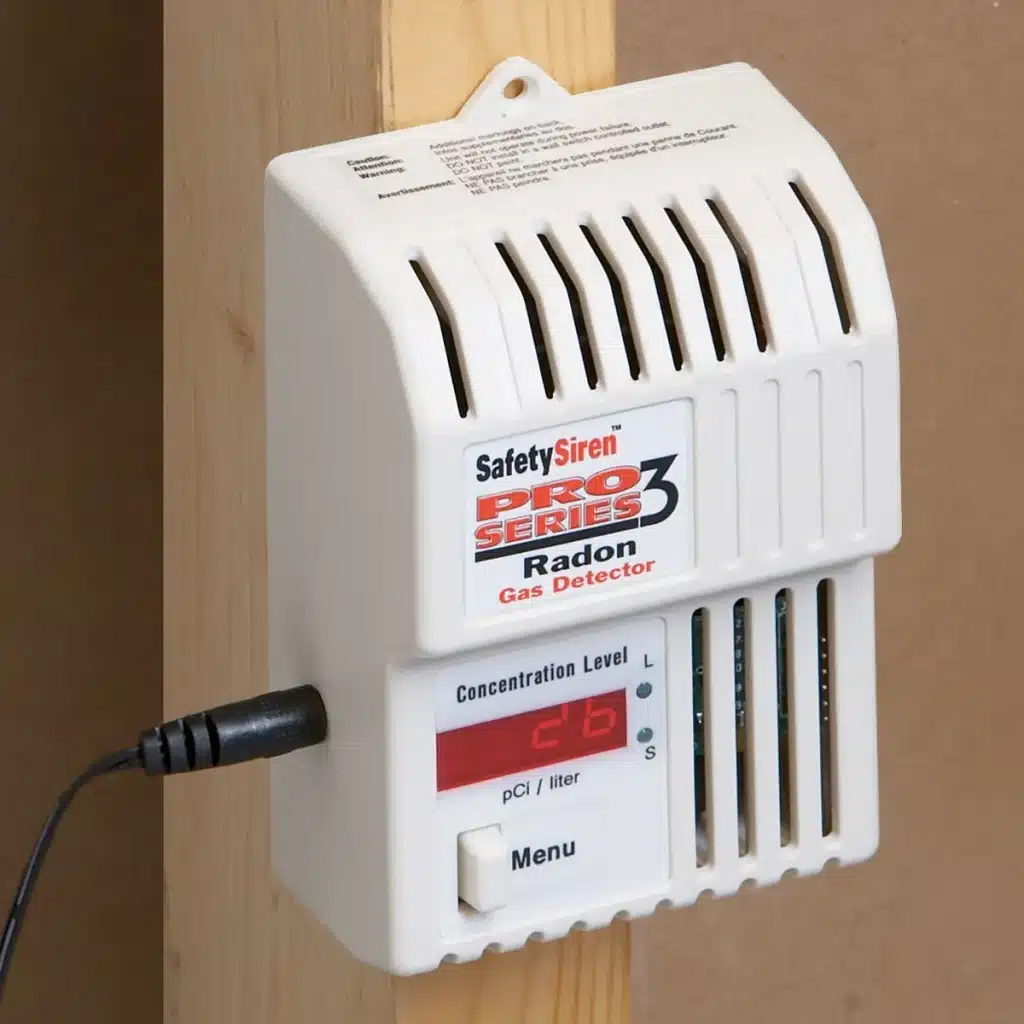

Detecting radon gas is essential since it cannot be seen, tasted, or smelled. The most reliable way to know if radon is present in a home or building is through testing. Various radon detection methods are available, ranging from short-term tests (lasting for a few days) to long-term tests (lasting for up to a year), which provide a more accurate assessment of average radon levels. These tests are typically easy to use and can be found in hardware stores or purchased online.
For homeowners concerned about radon, home testing kits offer a practical solution. These kits are placed in the lowest lived-in area of the home, where radon levels are likely to be highest, and then sent to a laboratory for analysis. It’s recommended to test for radon during different seasons, as levels can fluctuate throughout the year. For more comprehensive analysis, especially in areas known for high radon levels, hiring a professional radon tester can provide more detailed and accurate results.
Legal Standards and Safety Regulations

Internationally, there is a growing awareness of the risks associated with radon gas, leading to the establishment of various safety standards and guidelines. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other international bodies have set recommended action levels for indoor radon concentrations, urging national governments to adopt policies and regulations to protect public health. These recommendations are continuously updated as new research on radon risks becomes available.
Local regulations regarding radon safety can vary significantly. In some regions, radon testing is mandatory for certain types of buildings or during real estate transactions. Others have set specific radon concentration limits beyond which mitigation measures must be implemented. Homeowners and builders should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance and safety. In many cases, these laws not only aim to reduce health risks but also guide the construction of new buildings to prevent radon accumulation.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
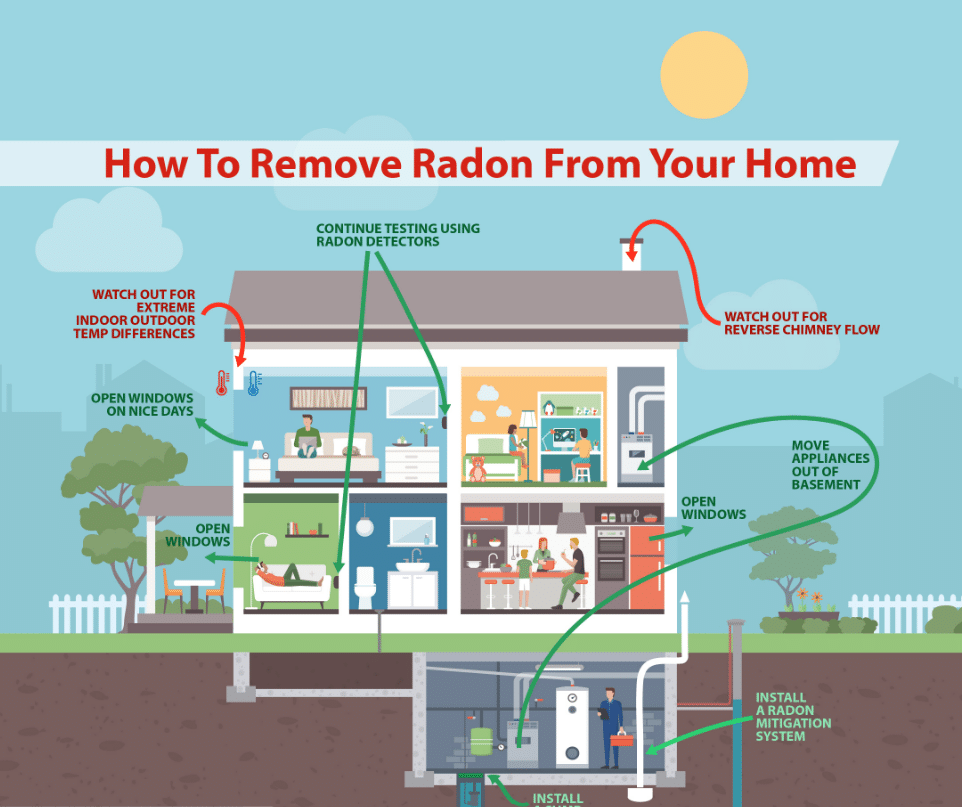
Once high levels of radon are detected, it’s crucial to implement mitigation strategies to reduce indoor radon levels. Professional radon mitigation services often use techniques like soil suction, which involves drawing radon from below the building and venting it outside. Sealing cracks in floors and walls and improving ventilation can also significantly reduce radon levels. These mitigation methods vary in complexity and cost, but they are vital for reducing the risk of lung cancer associated with radon exposure.
In addition to professional mitigation, there are several preventative measures homeowners can take. Simple steps like increasing ventilation, particularly in basements, and sealing cracks and openings in the foundation can help reduce radon entry. When building a new home, incorporating radon-resistant construction techniques is an effective way to prevent radon problems. These measures are especially important in areas known for high radon levels and can contribute significantly to long-term health and safety.
Case Studies on Radon Gas Incidents
Examining real-life case studies of radon gas incidents provides valuable insights into the risks and consequences of radon exposure. Residential examples often reveal how unsuspecting homeowners discovered high radon levels, sometimes only after a family member had been diagnosed with lung cancer. These cases underscore the importance of regular radon testing, as the gas can accumulate unnoticed over time, posing significant health risks. Many of these stories also highlight how proper mitigation techniques successfully reduced radon levels, safeguarding the occupants’ health.
In the industrial context, radon incidents can be even more dramatic. Workplaces like mines and construction sites, especially those involving earthworks, have reported elevated radon levels. These cases often lead to stricter safety regulations and the implementation of regular monitoring and mitigation measures. Industrial case studies serve as a stark reminder of the occupational hazards related to radon, particularly in industries involving underground work where radon concentration can be significantly higher.
Future of Radon Gas Research and Technology

The field of radon research is continually evolving, with new studies shedding light on the broader impacts of radon exposure and refining our understanding of safe exposure levels. Current research focuses not only on the health effects but also on identifying geographic areas at higher risk and improving prediction models for radon generation and accumulation. These studies play a crucial role in updating safety standards and informing public health policies.
Technological advancements are also revolutionizing the way we detect and mitigate radon. Innovations in detection technology are making radon testing more accessible and accurate, allowing for real-time monitoring of radon levels in homes and workplaces. On the mitigation front, newer, more efficient methods are being developed, reducing the cost and complexity of making buildings radon-safe. These technological strides, coupled with ongoing research, are key to managing radon risks and ensuring public health and safety in the future.
The Radon Gas Challenge
This comprehensive exploration of radon gas illuminates its nature, sources, associated health risks, and the critical importance of detection and mitigation. Understanding radon is not just about recognizing its presence but involves actively engaging in testing and employing necessary measures to safeguard health and wellbeing. The evolving landscape of radon research and technology promises enhanced protection in the future. Everyone, from homeowners to industry professionals, plays a vital role in this endeavor, making informed decisions to tackle the challenge of radon gas effectively.


